fractional flow reserve normal values
Blockages that score above this threshold can be safely and adequately treated by medical therapy without the need for angioplasty. The normal value of FFR is unequivocally 1 for every coronary artery regardless of size.

Fractional Flow Reserve Coronary Flow Reserve And The Index Of Microvascular Resistance In Clinical Practice Radcliffe Cardiology
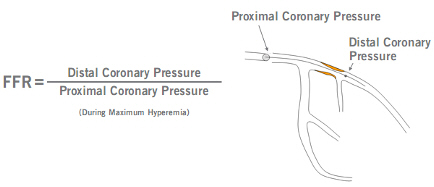
Fractional Flow Reserve for the Diagnosis of Flow-limiting Coronary Artery Disease Coronary stenosis severity and lesion-level ischaemia can be assessed invasively based on the myocardial fractional flow reserve FFR resting distal coronary pressure to aortic pressure ratio PdPa during hyperaemia and the ischaemic threshold 080 223132 see Figure 1.

. An FFR of 10 is widely accepted as normal. Although the normal value of 10 is well. Fractional flow reserve computed tomography FFR CT is a noninvasive means of estimating coronary ischemia using principles of fluid dynamics to create three-dimensional mathematic modeling of coronary flow pressure and resistance under varying hemodynamic conditions.
For example an FFR value of 080 means that the maximum blood flow in the coronary artery being measured is 80 of what it would be if the artery were completely normal. FFR is expressed as the reciprocal of normal maximal flow through a stenotic artery Fig. Stenoses with an FFR 080 are rarely associated with exercise-induced ischaemia.
Use and Value of Fractional Flow Reserve in Coronary Arteriography. This suggests the absence of epicardial vessel resistance to blood flow. Higher values indicate a non-significant stenosis whereas lower values indicate a significant lesion.
The authors provide values for evaluating the lesion with 075 or less being abnormal 075-08 being borderline and greater than 08 being normal. Fractional collateral flow is maximum recruitable collateral blood flow expressed as a fraction of normal maximal flow. A normal value for FFR is 10 regardless of the microcirculation status.
The aims of this. FFR value represents the fraction of the normal maximal myocardial flow that can be achieved despite the coronary stenosis. CT fractional flow reserve FFRCT is a physiologic simulation technique that models coronary flow from routine coronary CT angiography CTA.
FFRCT greater than 08 is normal 07608 is borderline and 075 or less is abnormal. FFRCT should always be interpreted in. FFR values less than 075 indicate that the narrowing has hemodynamic significance and revascularization should be performed.
CFR 20 represents a nonischemic value with an unknown normal value as CFR can change depending on existing conditions of the patient. An FFR 075 is associated with inducible ischemia specificity 100 whereas a value 080 indicates absence of inducible ischemia in the majority of patients sensitivity 90. Epub 2019 May 13.
To evaluate lesion-specific ischemia FFRCT is measured 2 cm distal to a stenotic lesion. FFR has a normal value of 10 for every patient and every coronary artery. Fractional flow reserve FFR measurement involves determining the ratio between the maximum achievable blood flow in a diseased coronary artery and the theoretical maximum flow in a normal coronary artery to determine the likelihood that the stenosis impedes oxygen delivery to the heart muscle.
A major limitation of classical flow reserve indexes such as coronary flow reserve CFR blood flow velocity and absolute flow is the wide variability of normal values. Conversely in patients with detected atherosclerosis elsewhere 50 of the coronary arteries will have a lower than normal FFR and on 10 the FFR will be lower than the ischemic threshold 9. Clinical and anatomical coronary CTA findings should be correlated to FFR CT.
The normal value of FFR is 10. The higher the fractional flow reserve value the lower the chances of any abnormality. Studies have shown that an FFR value less than 075 or 080 corresponds to inducible ischemia and most likely will require interventional treatment.
In clinical trials however a cut-off point of 075 to 080 has been used. The lowest recorded value for a normal coronary was reported at 094 9. If this ratio is above approximately 03 there is a 6-fold lower chance of a myocardial infarction occurring during a follow-up of 3-5 years.
However for the evaluation of this novel technique the FFR is. Usually a fractional flow reserve value of one is accepted as normal whereas values lower than 075 generally indicate a heart attack. Pw - PvPa - Pv.
Fractional flow reserve FFR defined as the ratio of maximum flow in the presence of a stenosis to normal maximum flow is a lesion-specific index of stenosis severity that can be calculated by simultaneous measurement of mean arterial distal coronary and central venous pressure Pa Pd and Pv respectively during pharmacological vasodilation. In contrast FFR has an absolute normal value of 10 for every artery every patient and every condition. FFR values greater than 08 indicate that the narrowing has minimal hemodynamic significance and no revascularization should be performed.
The FFR-CT is calculated by dedicated software and with a FFR cutoff value of 08 FFR-CT results in a sensitivity of 78 and specificity of 87 compared with FFR 38 39. For example an FFR of 075 means that the stenotic vessel only provides 75 of the normal expected flow in the theoretical absence of the stenosis. A normal value of IMR is below 3019 Fractional flow reserve Definition Fractional flow reserve FFR is defined as the ratio of the maximal blood flow achievable in a stenotic vessel to the normal maximal flow in the same vessel which represents the fraction of maximum flow that can still be maintained despite the presence of the stenosis.
Fractional flow reserve FFR is the ratio of maximum blood flow distal to a stenotic lesion to normal maximum flow in the same vessel. FFR Pd Pa Pd pressure distal to the lesion blockage. The fractional flow reserve value is displayed on the monitor attached.
Normal values of CFR widely vary from patient to patient and strongly depend on the current hemodynamic state as shown in chapter 9 extent of collaterals chapter 16 and. This provides guidance for the clinician in situations when it is not clear if a lesion of intermediate angiographic severity is the cause of ischaemia.

The Distribution Of Values For Fractional Flow Reserve Ffr Download Scientific Diagram
Fractional Flow Reserve Ffr Cathlab Com

Fractional Flow Reserve Concepts Applications And Use In France In 2010 Thoracic Key

Accuracy Of Intravascular Ultrasound Based Fractional Flow Reserve In Identifying Hemodynamic Significance Of Coronary Stenosis Circulation Cardiovascular Interventions

Fractional Flow Reserve Coronary Flow Reserve And The Index Of Microvascular Resistance In Clinical Practice Radcliffe Cardiology

Fractional Flow Reserve An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

Fractional Flow Reserve To Guide Coronary Revascularization Semantic Scholar

Fractional Flow Reserve Coronary Flow Reserve And The Index Of Microvascular Resistance In Clinical Practice Radcliffe Cardiology

Fractional Flow Reserve Simple Knowledge Base

Fractional Flow Reserve Ffr In The Presence Of Serial Stenoses In A Download Scientific Diagram

Optimizing The Technique For Invasive Fractional Flow Reserve To Assess Lesion Specific Ischemia Circulation Cardiovascular Interventions

Conceptual Plot Of The Fractional Flow Reserve Ffr Coronary Flow Download Scientific Diagram

Diagnostic Accuracy Of Diastolic Fractional Flow Reserve For Functional Evaluation Of Coronary Stenosis Diastole Study Jacc Asia
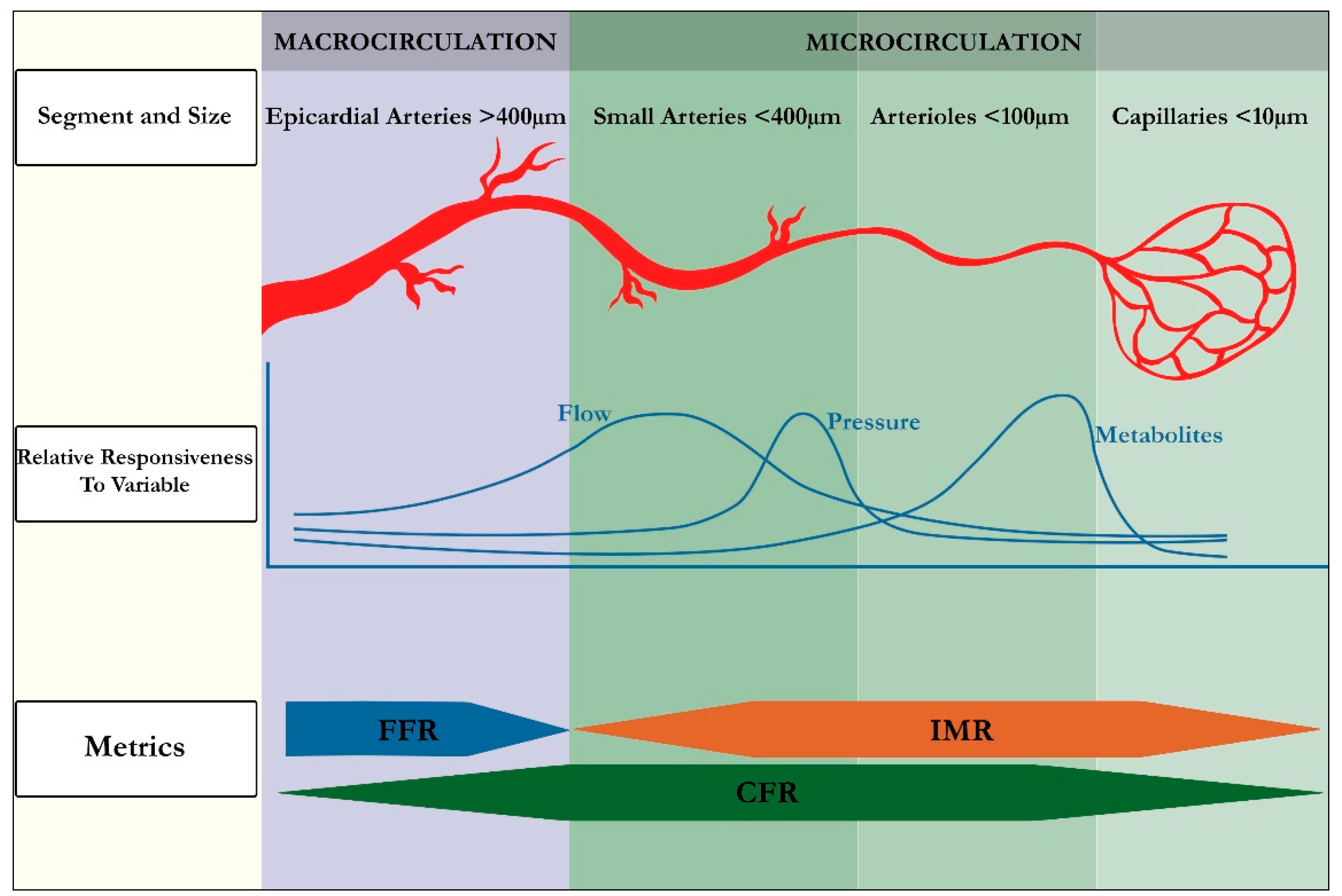
Jcm Free Full Text Invasive Evaluation Of The Microvasculature In Acute Myocardial Infarction Coronary Flow Reserve Versus The Index Of Microcirculatory Resistance Html

Coronary Flow Reserve And Fractional Flow Reserve Uses Complications
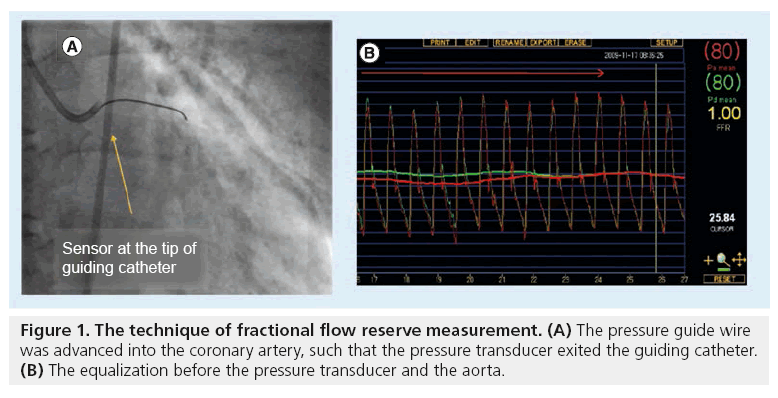
Fractional Flow Reserve A New Paradigm For Diagnosis And Management Of Patients With Coronary Artery Disease
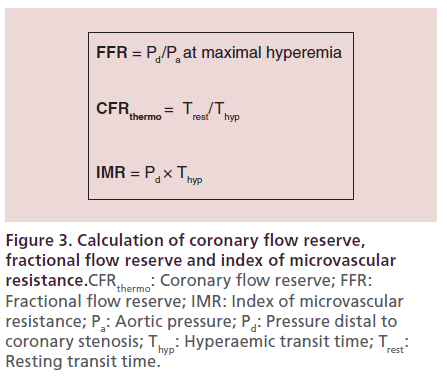
Current Frontiers In The Clinical Research Of Coronary Physiology
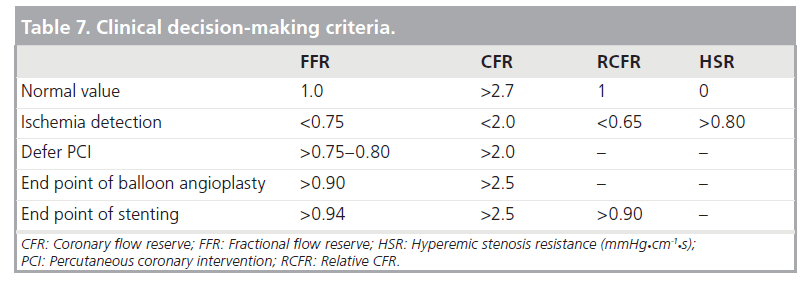
Role Of Fractional And Coronary Flow Reserve In Clinical Decision Making In Intermediate Coronary Lesions